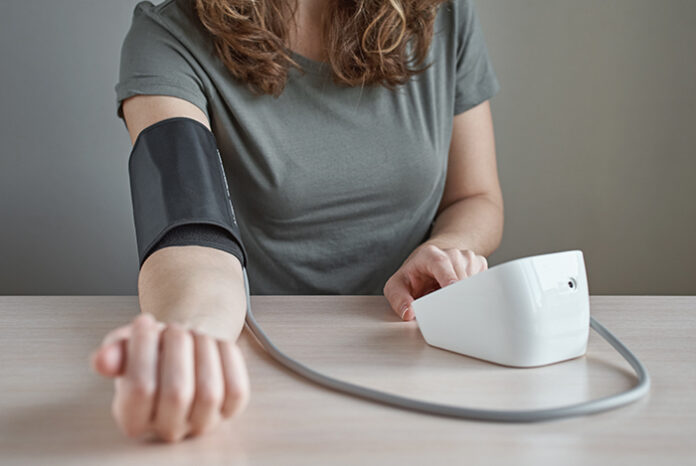

Blood pressure is a crucial health indicator, reflecting the force of blood against the walls of your arteries. High blood pressure, or hypertension, is a silent but dangerous condition that increases the risk of heart, kidney, and brain diseases.
Causes of High Blood Pressure
High blood pressure, or hypertension, is a prevalent condition that can lead to severe complications if not managed effectively. Understanding its causes is crucial for prevention and treatment.
1. Genetic Factors:
- Family History: Individuals with a family history of hypertension are at a higher risk.
- Genetic Mutations: Specific genetic mutations can lead to high blood pressure.
- Ethnicity: Certain ethnic groups are more prone to develop hypertension.
2. Lifestyle Choices:
- Poor Diet: Consuming foods high in sodium and low in essential nutrients can elevate blood pressure.
- Physical Inactivity: Lack of exercise contributes to weight gain and hypertension.
- Tobacco Use: Smoking or using tobacco products can temporarily raise blood pressure and damage arteries over time.
3. Underlying Health Conditions:
- Kidney Disease: The kidneys play a vital role in regulating blood pressure; kidney disease can disrupt this function.
- Diabetes: People with diabetes are at a higher risk of hypertension due to insulin resistance.
- Sleep Apnea: This sleep disorder, characterized by interrupted breathing, can lead to high blood pressure.
4. Age and Gender:
- Age: Blood pressure tends to increase with age due to the hardening of arteries.
- Gender: Men are generally at a higher risk of developing high blood pressure at a younger age, while the risk increases for women after menopause.
5. Environmental Factors:
- Stress: Chronic stress can contribute to hypertension, though it is not a direct cause.
- Excessive Alcohol: Drinking alcohol in moderation can potentially lower blood pressure, but excessive consumption is harmful.
6. Medications and Supplements:
- Prescription Drugs: Some medications, like birth control pills and corticosteroids, can raise blood pressure.
- Over-the-Counter Medications: Non-prescription drugs, like cold remedies, can increase blood pressure.
- Supplements: Certain dietary supplements can interact with medications and affect blood pressure.
7. Hormonal Issues:
- Thyroid Problems: Both hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism can cause high blood pressure.
- Adrenal Disorders: Conditions affecting the adrenal glands can lead to hypertension.
Natural Supplements for Blood Pressure
Using natural supplements can be an effective way to prevent and manage high blood pressure. However, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new supplement regimen.

-
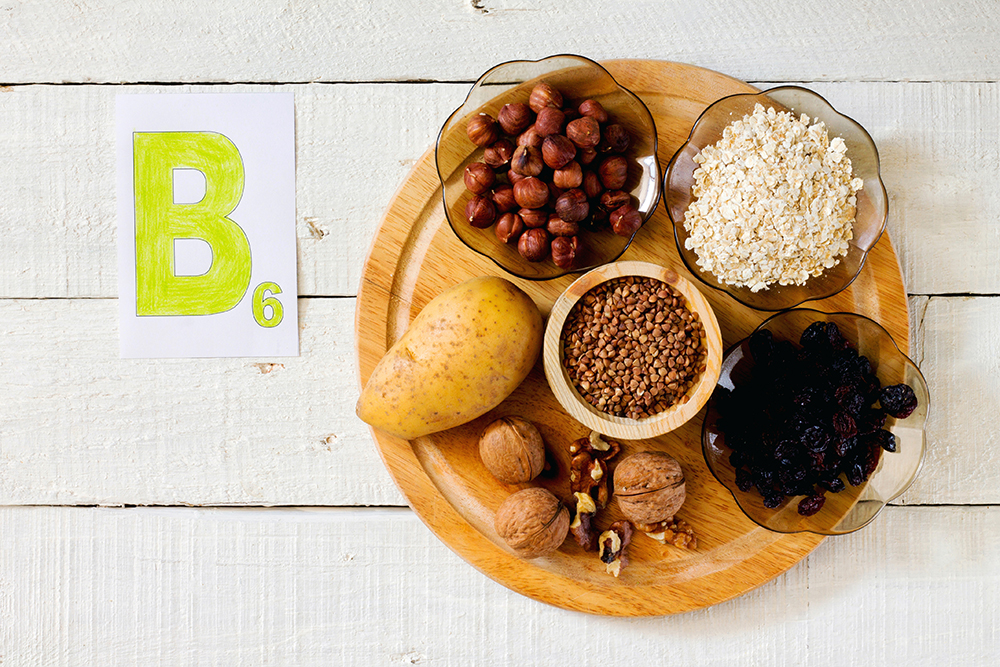
1. B Vitamins:
- How They Work: B vitamins, particularly folic acid (B9) and B6, help regulate homocysteine levels in the blood, reducing the risk of vascular diseases. Elevated homocysteine can damage arterial linings, leading to hypertension.
- Usage: Incorporating B vitamins through diet or supplements supports heart health. Consultation for appropriate dosage is advised.
- Contraindications: Individuals with liver disease, cancer, or other health conditions should avoid excessive B vitamins.
- Drug Interactions: B vitamins may interact with antiepileptic medications, chemotherapy drugs, and certain antibiotics.
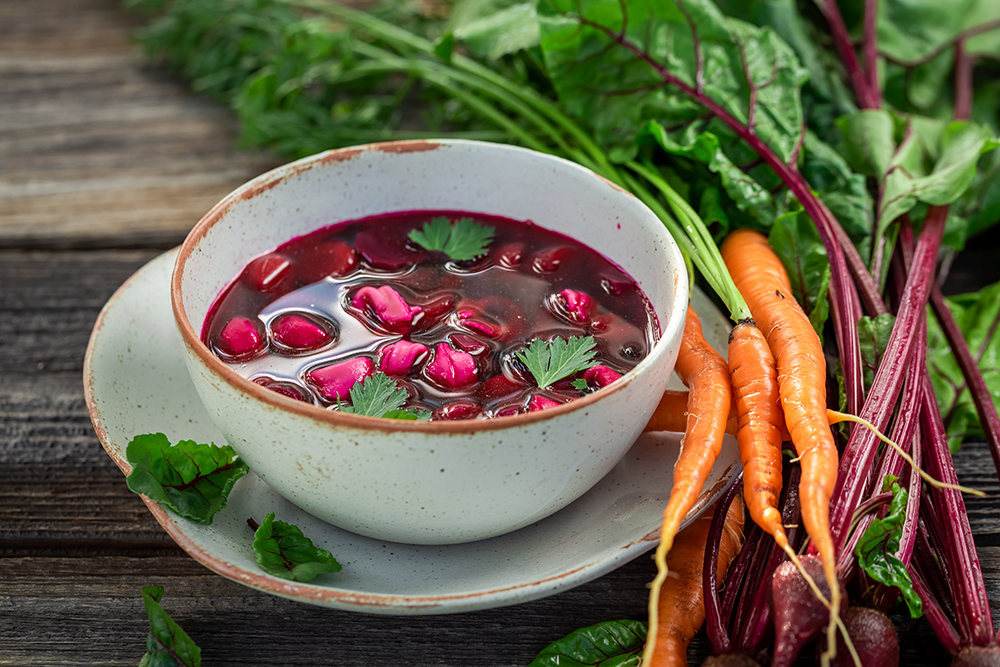

2. Beetroot:
- How It Works: Beetroot is rich in dietary nitrates, converted into nitric oxide in the body. Nitric oxide relaxes and widens blood vessels, improving blood flow and lowering blood pressure.
- Usage: Beetroot juice or supplements can provide necessary nitrates. Consult healthcare professionals for guidance.
- Contraindications: People with kidney stones or iron metabolism issues should exercise caution.
- Drug Interactions: Beetroot may amplify the effects of nitrate medications and blood pressure drugs.
3. CoQ10 (Coenzyme Q10):
- How It Works: CoQ10 supports energy production in cells, improves endothelial function, reduces arterial stiffness, and has a mild antihypertensive effect.
- Usage: Supplements are available in various forms. Dosage recommendations vary; medical advice is crucial.
- Contraindications: Individuals with diabetes, liver diseases, or undergoing chemotherapy should consult before using CoQ10.
- Drug Interactions: CoQ10 may interact with blood thinners, thyroid medications, and chemotherapy drugs.
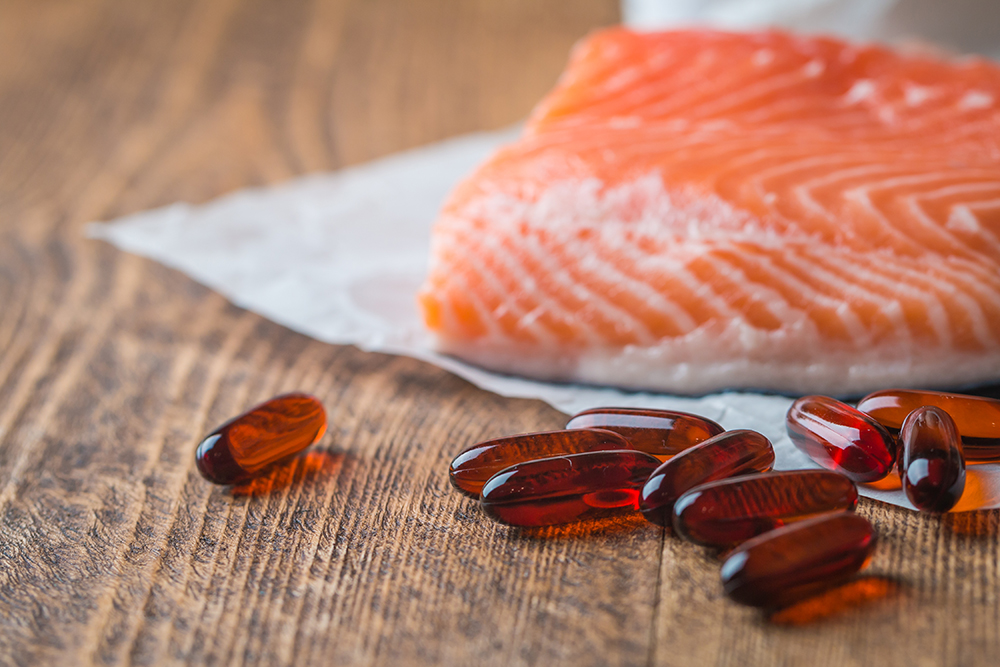

4. Fish Oil:
- How It Works: Fish oil contains omega-3 fatty acids, lowering blood pressure by reducing inflammation, decreasing blood clotting, and improving blood vessel health.
- Usage: Fish oil supplements or fatty fish in the diet can provide these benefits. Consult for dosage.
- Contraindications: People with fish or shellfish allergies, bleeding disorders, or diabetes should avoid fish oil unless advised.
- Drug Interactions: Fish oil may interact with blood thinners, blood pressure medications, and contraceptive pills.

5. Garlic:
- How It Works: Garlic’s allicin has anti-inflammatory and lipid-lowering properties, relaxing blood vessels and lowering blood pressure.
- Usage: Garlic supplements or fresh garlic can be beneficial. Consult for appropriate dosages and to avoid medication interactions.
- Contraindications: Individuals with bleeding disorders, stomach ulcers, or thyroid problems should be cautious.
- Drug Interactions: Garlic may interact with blood thinners, HIV medications, and certain antibiotics.

6. Magnesium & Potassium:
- How They Work: Magnesium relaxes blood vessels, and potassium balances sodium effects, maintaining healthy blood pressure levels.
- Usage: Dietary sources or supplements can provide these minerals. Adhere to recommended daily allowances and consult healthcare providers.
- Contraindications: People with kidney diseases, heart conditions, or on potassium-sparing diuretics should avoid excessive intake.
- Drug Interactions: These minerals may interact with diuretics, heart medications, and muscle relaxants.

7. Probiotics:
- How They Work: Probiotics improve gut health, influencing blood pressure regulation by possibly regulating the renin-angiotensin system.
- Usage: Probiotic supplements or foods like yogurt can be beneficial. Consult for the right strains and dosages.
- Contraindications: Individuals with weakened immune systems should be cautious.
- Drug Interactions: Probiotics may interact with antibiotics and immunosuppressive drugs.

8. Vitamin C:
- How It Works: Vitamin C relaxes blood vessels and improves endothelial function, leading to lower blood pressure.
- Usage: Supplements or vitamin C-rich foods can be incorporated. Consult healthcare providers for appropriate dosages.
- Contraindications: People with kidney stones, hemochromatosis, or kidney disorders should consult before taking vitamin C supplements.
- Drug Interactions: Vitamin C may interact with chemotherapy drugs, statins, and blood thinners.
Lifestyle Changes
Supplements should be used alongside lifestyle modifications like adopting a healthy diet, engaging in regular exercise, managing stress, and, if necessary, taking prescribed medications.
Managing blood pressure is vital for maintaining overall health. Natural supplements, combined with lifestyle changes, can offer support in preventing and controlling hypertension. Always consult with a healthcare provider before starting any supplement regimen to ensure it’s safe and right for you.










