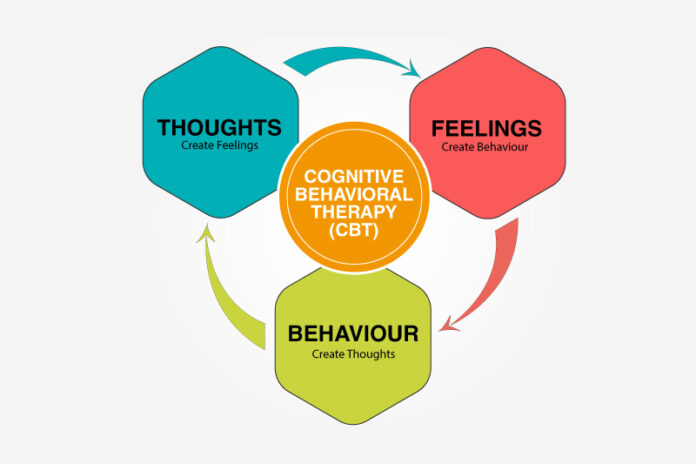
How Does CBT Work?
CBT operates on the principle that our thoughts, feelings, and behaviors are interconnected. By changing unhelpful thoughts and behaviors, we can improve our emotional well-being. CBT is typically short-term and goal-oriented, focusing on specific problems the individual is facing.
Key Components of CBT:
Identifying Negative Thoughts:
CBT helps individuals recognize distorted thinking patterns, such as catastrophizing (expecting the worst) or black-and-white thinking. By identifying these thoughts, individuals can challenge and replace them with more balanced perspectives.
Behavioral Activation:
CBT encourages positive behaviors that reinforce healthier thought patterns. For example, someone with depression might be encouraged to engage in activities they once enjoyed, helping to break the cycle of inactivity and low mood.
Cognitive Restructuring:
This involves questioning and reframing negative beliefs. For instance, if someone believes “I always fail,” CBT would help them recognize exceptions and develop a more realistic, positive belief like, “I sometimes succeed, and I can learn from setbacks.”
Exposure Therapy:
For individuals dealing with phobias or anxiety, CBT might include gradual exposure to feared situations, helping them build confidence and reduce avoidance behaviors.
Benefits of CBT
CBT is effective for a wide range of issues, including:
Anxiety Disorders: Helps manage panic attacks, social anxiety, and generalized anxiety disorder.
Depression: Encourages positive thinking and behaviors to combat depressive symptoms.
Stress Management: Provides tools to handle everyday stress and improve resilience.
Phobias and PTSD: Gradual exposure and cognitive restructuring help reduce fear and trauma responses.
CBT is also versatile, and adaptable for individuals, group therapy, and even online formats.
What to Expect in a CBT Session
Who Can Benefit from CBT?
Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy is a highly effective method for addressing a range of mental health issues by focusing on the relationship between thoughts, feelings, and behaviors. Whether you’re struggling with anxiety, depression, or stress, CBT offers practical strategies to help you regain control and improve your quality of life.












